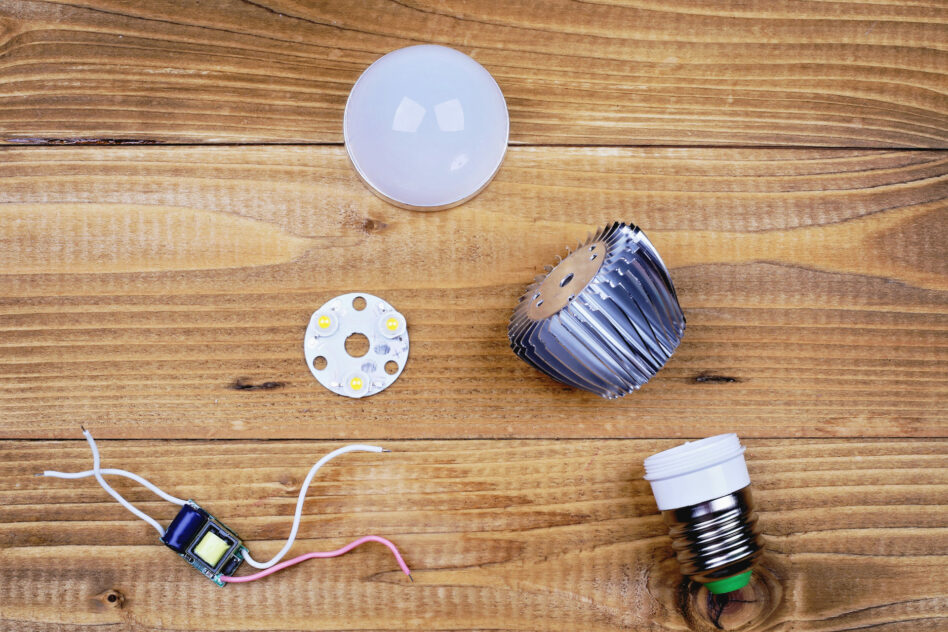
Light-emitting diode (LED) light bulbs are becoming more and more popular due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan. Understanding the components that make up an LED bulb can help you make informed choices when selecting bulbs for your home or business.
LED Chip
An LED chip is a tiny electronic device made from semiconductor materials, such as aluminum gallium and gallium nitride. A small amount of foreign material, such as gallium arsenide or silicon, is combined with the semiconductor. This mixture creates a boundary between two regions, called a p-n junction.
The n-region, which has extra electrons, is the area that’s negatively charged. The other region, called the p-region, has too few electrons and is positively charged.
When these two regions come into contact, they form an area called the depletion zone. This zone has few electrons. The depletion zone happens when the negatively charged electrons from the n-region move toward the positively charged holes in the p-region.
Once you apply voltage to the junction, the free electrons move across the region, creating a flow of electrical current. This releases energy in the form of light.
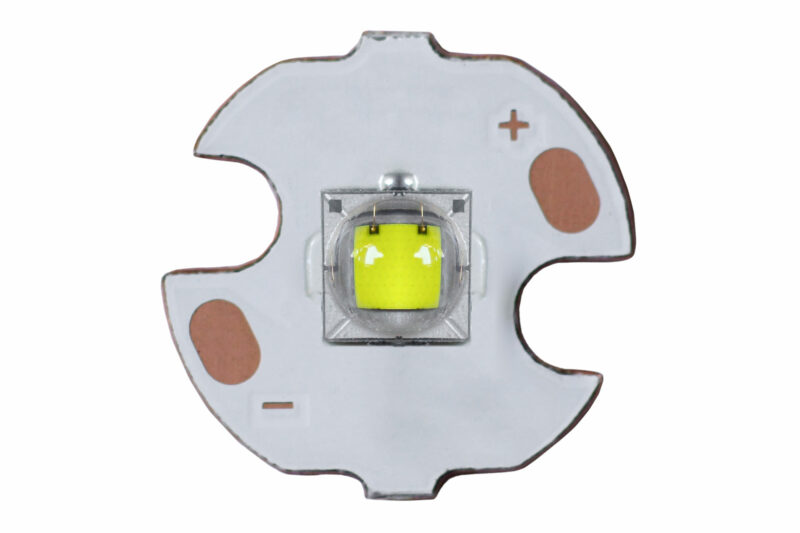

How Do LED Chips Work?
LED chips use a process called electroluminescence, which is the production of light from the semiconductor material when electricity passes through it.
When electricity flows through these materials, it causes the electrons inside them to move around and get excited. Once the electrons go back to their original positions, they emit light.
LED chips convert almost all the energy they consume into light, making them more efficient and longer-lasting than traditional bulbs.
Also, the material affects the color of the light that LED chips emit. Gallium nitride is frequently used as a semiconductor material to create blue or green light. Red light is generated by using aluminum gallium arsenide.
Heat Sink
Most of the electrical energy fed into an LED light bulb transforms into light energy. However, a small amount is converted into heat, which can damage the bulb over time.
Overheating can shorten a light bulb’s lifespan if it’s not controlled effectively. This is where heat sinks come in handy, as they help dissipate the heat generated by the LED light bulb.
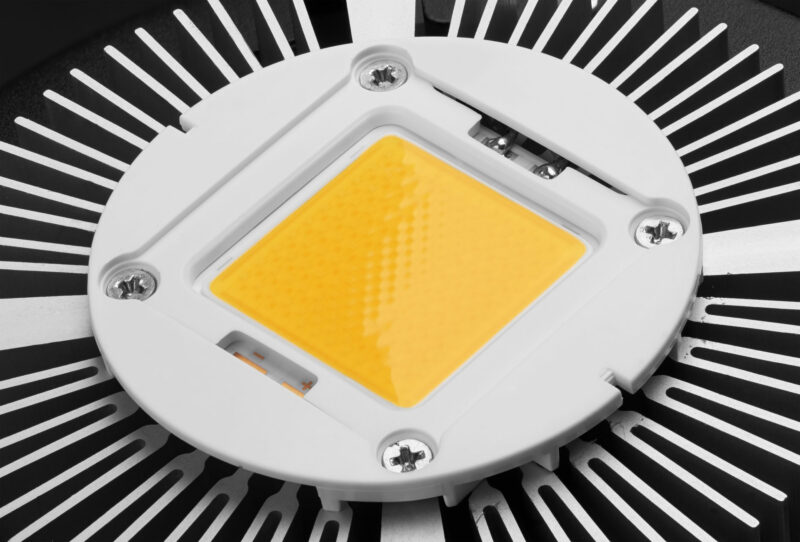

Heat sinks are usually made of materials that are good at absorbing and releasing heat, such as aluminum or copper. Ceramics or graphite are also used to make heat sinks, but they’re not that common.
Lens
A lens is a transparent or translucent material placed over LED chips that helps shape, focus, and direct the light emitted by the LED chips. They’re often used to focus light on a certain area or a certain angle.
Lenses are usually made from glass, plastic, or silicone. They can come in different sizes and shapes, depending on the needed application. Some lenses can help create a narrow and focused beam of light. On the other hand, some lenses diffuse a wider spread of light.
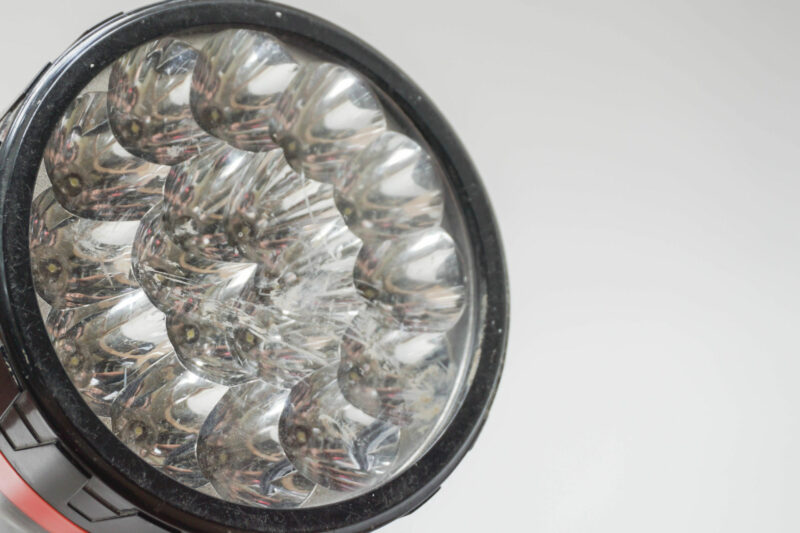

Aside from controlling the direction and distribution of light, lenses can also protect the light bulb from external damage, such as moisture and dust. Additionally, lenses also provide a clean and finished look with the use of different designs and sizes.
Lenses can also help improve the light bulb’s efficiency by maximizing the light directed where it’s needed.
Base
The base of an LED light bulb connects the light bulb to the electrical circuit/power source. They contain two or more metal pins or contacts that fit into a socket. Essentially, it helps provide the necessary electrical contact for the LED light bulb.
The base can also serve as a physical connection point between the LED light bulb and a light fixture or lamp. A secure base can provide stability to make sure that the LED light bulb does not move or shift while in use.
High-quality materials such as brass, stainless steel, and aluminum are often used for bases. They ensure that the base can withstand high temperatures.
The shape and the size of the base affect the overall appearance of the light bulb. Depending on the application, the overall design may also affect the direction and distribution of the light output.
Enclosure
The primary function of an enclosure is to provide a protective cover for the internal components of the LED light bulb. It protects the bulb’s delicate internal components from being damaged by moisture, dust, and other external factors.
The enclosure serves quite a few other functions. First, it provides a mount for the bulb to fit into. The mount is designed to hold the light bulb securely in place. Additionally, the enclosure can also direct and diffuse the light emitted by the LED chips.
Finally, the enclosure can be used to shape the light emitted by the LED chip. This can improve the quality of the light emitted by the light bulb.
Driver
The driver is an electronic device that regulates the power supplied to the LED chips. Its main function is to ensure that the LED chips receive the appropriate amount of electric power. Feeding the LED chips with too little or too much electric power may damage them over time.
The driver converts the AC power from the power supply to DC power. The LED chips have a low voltage and a current rating, so the driver steps down the voltages and regulates the current to the appropriate level.
Simply put, it takes power from the primary electrical source and delivers it to the LED chips in a way they can safely handle. This process guarantees that the LED chips can operate more efficiently and safely.
Aside from this, the driver also protects the LED chips from overvoltage, overcurrent, and overheating. Some LED bulbs have dimming capabilities, and a driver can be programmed to vary the current and voltage that the LED chips receive.






