LED lights are generally safe and economical, but improper use may impact your health. Blue light exposure can disrupt sleep patterns, while flickering lights can cause migraines and dizziness. Understanding these potential health risks can help you minimize their impact.
Health Impact of LED Lights: Quick Overview
Light Emitting Diode, or LED, is a type of energy-efficient lighting that has become popular in recent years. Compared with incandescent bulbs, LED lights are a more cost-effective option for home and office use.
LED lights are more efficient and can last longer than traditional light bulbs. Additionally, their versatility allowed for their use even on televisions or mobile phones. However, there are potential health risks associated with their usage.
Exposure to blue light poses the highest level of risk because it can significantly interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and cause other health issues. Moreover, LED lights may cause headaches, dizziness, and eye fatigue, especially for light-sensitive people.
By learning about the benefits of LED lights and the potential health risks associated with their use, you can take precautions to reduce LED light exposure and minimize the risk of health problems.
Benefits of LED Lights
LED lights offer numerous benefits compared to traditional lighting sources. In this section, we’ll explore some of the advantages of using LED lights:
Energy Efficient
LED lights produce little heat, making them more energy efficient than traditional light bulbs. They can transform up to 95% of energy into light. Meanwhile, other kinds of light bulbs convert only 10% of the energy into light, while the rest transforms into heat.
Durability
Traditional bulbs have fragile components that easily break or wear out, while LED lights use durable, solid-state lighting technology. They’re commonly enclosed in shatter-resistant material, protecting their internal parts from environmental factors and impact.
Long Lifespan
They don’t rely on a filament or gas that deteriorates or burns out with use over time. For this reason, LED lights have a significantly longer lifespan and can last up to 50,000 hours.
Eco-Friendly
LED lights are a safer and more environmentally-friendly alternative as they don’t contain hazardous materials like mercury. They’re also recyclable, making them a suitable option for lighting.
Cost-Effective
Compared to traditional lighting sources, LED lights are more cost-effective because of their high energy efficiency. Due to this, they result in lower electricity bills and reduced energy consumption.
Potential Health Impacts of LED Light Use
As LED lights have become increasingly popular, their potential impacts on human health have sparked discussions. Despite its advantages, the usage of LED lights can have potential health risks associated.
In this section, we’ll explore the health impacts of LED lights and provide tips on how to minimize them:
Blue Light Exposure
Blue light is a high-energy light with a short wavelength emitted by electronic devices, LED lights, and the sun. It helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, or sleep-wake cycle, by suppressing melatonin production.
Exposure to blue light during the day can elevate mood, increase alertness, and enhance cognitive functions. Moreover, blue light exposure in the morning can help regulate your body’s sleep-wake, allowing you to sleep better at night.
But excessive exposure can have adverse effects on the body. Firstly, it disrupts our natural sleep-wake cycle, which could lead to difficulties falling or staying asleep. Too much exposure to blue light inhibits melatonin production, which can cause insomnia and other sleep issues.
Secondly, one research has suggested that blue light exposure at night may be associated with an increased risk of health problems.
Another study revealed that exposure to blue light at night causes altered glucose metabolism. This increases hunger, leading to weight gain and insulin tolerance.
Finally, another study found a connection between prolonged blue light exposure and increased depressive symptoms.
If you’re having trouble falling or staying asleep, reducing your exposure to blue light can help. Let’s explore some of the most effective ways to reduce blue light exposure and promote better health:
- Use “night mode” or “night shift” on your devices. Most modern electronic devices have these settings to reduce the amount of blue light emitted by the screen.
- Spend more time outdoors during the day. Increasing your exposure to natural light can help regulate your circadian rhythm.
- Avoid using your electronic devices at least one hour before your bedtime. Doing this gives your body some time to adjust to lower light levels.
- Blue light filters are available for your glasses or electronic devices. These can significantly reduce the amount of blue light entering your eyes.
- To prepare your body for sleep, consider using dimmer lights and lamps. Doing this can help you wind down and relax before bedtime.
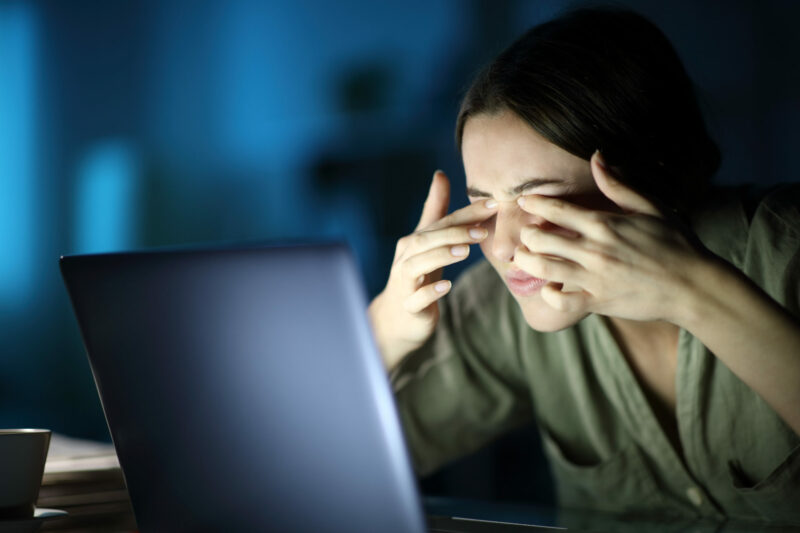

Eye Strain and Fatigue
Eye strain and fatigue can occur when your eyes are overused, resulting in discomfort and tiredness. These conditions can happen when you focus on something for prolonged periods without taking breaks.
LED light exposure can pose a significant issue, particularly for individuals who spend extended periods in front of electronic devices. LED screens emit high-energy blue light that can scatter more easily within the eye. These can cause visual discomfort and reduce visual acuity.
Eye strain and fatigue can manifest as a range of uncomfortable symptoms. One of the most common signs is having dry eyes, which can occur when you blink less frequently while looking at a screen.
In addition to dry eyes, prolonged exposure to LED screens can lead to headaches, blurred vision, and difficulty focusing. Some individuals may also experience neck or shoulder pain and general physical tiredness.
These symptoms are common for people who spend long periods in front of digital screens, such as students, gamers, and office workers. If you spend a lot of time in front of electronic devices or LED lights, it’s essential to take steps to reduce strain and fatigue:
- Reduce the brightness of your screen or LED lights to a comfortable level.
- Take frequent breaks and look away from the screen or LED lights every 20 minutes.
Keep the 20-20-20 rule in mind: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and look at something 20 feet away.
- Blink frequently to keep your eyes from getting dry.
- Install anti-glare filters on your screens or use glasses with anti-reflective coating.
- Adjust your display settings to lessen blue light emissions.
- Ensure that the lighting in your space is not too bright or too dim.
- Use ambient lighting whenever possible.
- Maintain a comfortable distance from your screen or LED lights to reduce eye strain.
Flicker
Another potential health risk associated with LED lights is flicker, which can cause dizziness and headaches in some people. Flicker is when a light rapidly gets brighter and darker in repeated succession, which makes it look like it’s flashing quickly.
Although all lights flicker to some extent, some LED lights may flicker at a higher frequency than traditional lights. It can be more noticeable and disturbing to some people. It can be especially true for those with specific medical conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, or vestibular disorders.
For instance, photosensitive epilepsy can be triggered by flashing lights if someone has a history of seizures. Furthermore, looking at screens and LED lights for a long time can tire your eyes, causing blurry vision and dry eyes. For the same reason, flickering lights can also cause visual migraines in some people.
If you’re concerned about the risks associated with flickering LED lights, there are several measures you can take:
- Choose LED lights with a high-frequency driver.
- Use dimmer switches designed to work with LED lights.
- Position the lighting where it doesn’t shine directly on your eyes.
- Take regular breaks from staring at screens or LED lights.
- Adjust the brightness and contrast on your electronic devices to reduce flicker.
- Consider using anti-glare filters on your electronic devices.
- If you experience symptoms related to flickering lights, consult a healthcare professional.






